Did you know that more than 80% of plug-in electric vehicle charging happens at home?
This makes perfect sense when you consider that charging your electric car at home is the most affordable and efficient way to keep your EV’s battery topped up. However, many new EV owners face a crucial decision when setting up their home ev charger – especially when comparing standard Level 1 chargers that can take a staggering 40-50 hours to charge from empty to 80%, versus a Level 2 home EV charger that completes the same task in just 4-10 hours.
For businesses and professionals investing in electric vehicle infrastructure, understanding the fundamentals of home EV chargers is essential. Additionally, Level 2 chargers offer valuable features beyond faster charging times, including hardwiring options, longer cords for flexible placement, and smart apps for monitoring battery life and charge times. When we consider that home charging allows you to start each day with a fully charged vehicle, selecting the right equipment becomes even more critical.
In this guide, we’ll walk through everything you need to know before purchasing a home EV charger – from electrical requirements and installation considerations to smart features and long-term scalability, ensuring you make an informed decision that avoids costly mistakes down the road.
Understand the Basics of Home EV Charging
Setting up an effective home charging solution requires understanding the fundamentals of EV charging technology. For businesses like Xeravolt looking to provide professional charging solutions, comprehending these basics is crucial for delivering value to clients.
Level 1 vs Level 2: What’s the difference?
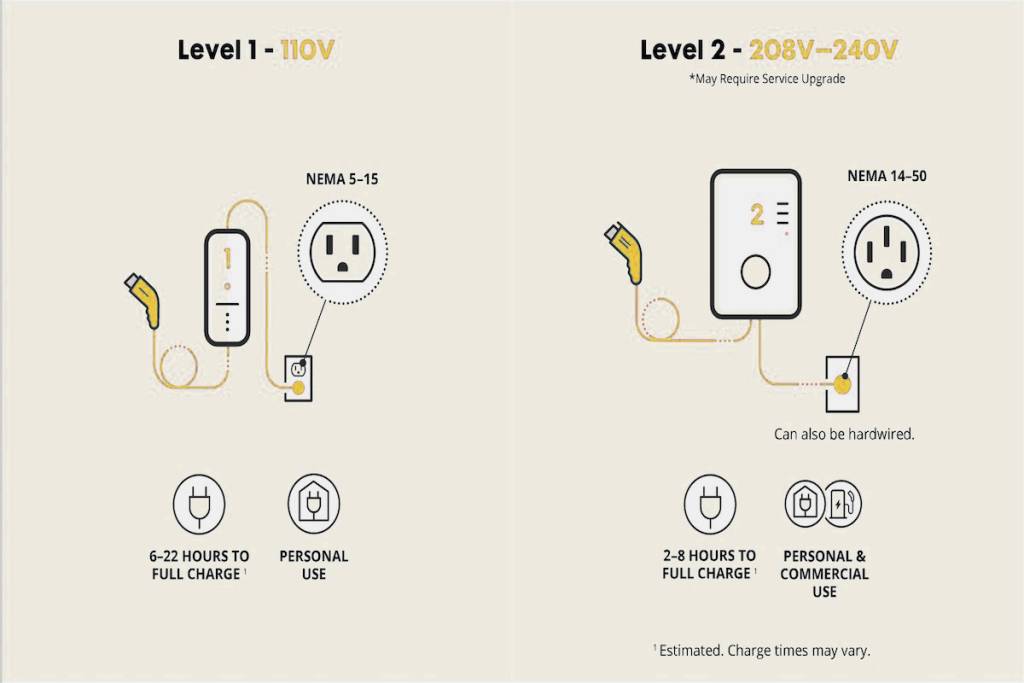
The distinction between Level 1 and Level 2 home EV chargers lies primarily in their power output, which directly affects charging speed:
Level 1 Charging:
- Operates through standard 110-volt household outlets
- Provides approximately 2-5 miles of range per hour of charging
- Comes standard with most electric vehicles
- Takes 40-50+ hours to charge a battery electric vehicle (BEV) to 80% from empty
- Ideal for plug-in hybrid vehicles with smaller batteries or low daily mileage needs
Level 2 Charging:
- Requires a 220-volt outlet (similar to what powers clothes dryers)
- Delivers about 10-60 miles of range per hour, depending on the specific charger and vehicle
- Charges approximately 6-8 times faster than Level 1 equipment
- Completes a full charge from empty in just 4-10 hours for most BEVs
- Requires professional installation by a certified electrician
How EV charging works at home
Home EV charging operates through a relatively straightforward process. Essentially, an EV charging station connects to your electrical grid and transfers electricity to your vehicle’s battery. Most passenger electric vehicles feature a built-in SAE J1772 charge port (also known as the J plug), allowing them to connect to standard home charging equipment.
During the charging process, alternating current (AC) from your home’s electrical system flows through the charging cable into your vehicle. Once inside the vehicle, an onboard converter transforms this AC power into direct current (DC) that can be stored in the battery.
The charging time varies based on three primary factors:
- The power output of your charging station
- Your vehicle’s battery capacity
- Your current battery level
For professional installations, it’s worth noting that all charging equipment should be UL certified to ensure safety and compliance with industry standards.
Why most EV owners prefer home charging
According to J.D. Power research, a remarkable 83% of electric vehicle owners prefer charging at home. This overwhelming preference stems from several significant advantages:
First, home charging offers unmatched convenience. Rather than hunting for public stations or waiting in lines, EV owners simply plug in when they arrive home. This seamless integration into daily routines makes EV ownership practically effortless.
Second, home charging typically costs significantly less than public options. Many utility companies offer special tariffs and incentives for EV owners, further reducing costs. Additionally, charging during off-peak hours (usually overnight) can lead to substantial savings.
Third, home charging provides complete control over the charging schedule. Whether you prefer overnight charging during off-peak hours or topping up during the day, the choice is entirely yours. Smart chargers with Wi-Fi connectivity allow monitoring and scheduling via smartphone apps, offering unprecedented convenience.
Lastly, home charging eliminates range anxiety by ensuring you start each day with a full battery. This peace of mind represents one of the greatest benefits of home EV charging.
Evaluate Your Home’s Electrical Capacity
Before installing a home EV charger, assessing your electrical infrastructure is crucial for both safety and optimal performance. For businesses like Xeravolt providing professional EV charging solutions, understanding these electrical requirements helps deliver reliable installations to clients.
Check your panel’s amperage and available circuits
The first step in evaluating electrical capacity involves examining your home’s electrical service panel. Most residential properties have either 100-amp or 200-amp service panels, with newer homes typically featuring the latter. For a standard Level 2 home EV charger installation, you’ll need:
- A dedicated 40-50 amp circuit for a 32-40 amp charger
- At least 25% spare capacity in your electrical panel
- Available physical space for a new circuit breaker
Professional electricians should perform a load calculation to determine if your panel can handle the additional demand. This calculation considers all existing electrical loads and the proposed EV charger load to ensure your system won’t become overloaded.
Remember that the National Electrical Code (NEC) requires EV circuits to be sized at 125% of the continuous load. Therefore, a 32-amp charger requires a 40-amp circuit breaker, while a 40-amp charger needs a 50-amp breaker.
Understand load management and circuit sharing
If your electrical panel is approaching capacity, several intelligent solutions can still enable home EV charger installation:
- Dynamic Load Management (DLM) – These systems monitor whole-house energy consumption in real-time and automatically adjust EV charging rates to prevent circuit overloads. For businesses installing multiple chargers, DLM technology provides a cost-effective alternative to panel upgrades.
- Circuit sharing – Some advanced Level 2 home EV chargers can share circuits with other high-power appliances like dryers or ranges. These smart chargers detect when the primary appliance is operating and temporarily reduce or pause charging to prevent tripping breakers.
- Time-of-use scheduling – Programming your EV charger to operate during off-peak hours not only saves on electricity costs but can also help manage overall household electrical load by avoiding simultaneous operation of multiple high-demand appliances.
For Xeravolt’s B2B clients, recommending appropriate load management solutions demonstrates value beyond basic installation services, particularly for properties with limited electrical capacity.
When to consider an electrical upgrade
Certain situations clearly indicate the need for electrical service upgrades before installing a home EV charger:
- Your load calculation shows less than 25% spare capacity
- You have an older 60-100 amp service panel
- Your panel has no available spaces for new breakers
- You plan to install multiple EV chargers or high-powered (48+ amp) chargers
- Your existing panel shows signs of wear (corrosion, heat damage, burning odors)
Panel upgrades typically cost between $1,500-$4,000 depending on service size and complexity. While this represents a significant investment, it provides long-term value by enabling not just EV charging but future electrical needs.
For Xeravolt’s business clients, developing relationships with licensed electricians who can perform these upgrades creates a complete service offering. Additionally, being knowledgeable about local utility requirements for service upgrades positions your business as a comprehensive EV charging solution provider.
Importantly, electrical upgrades should be viewed as infrastructure investments rather than mere expenses. They increase property value, enhance safety, and future-proof homes for increasing electrification of transportation and home systems.
Choose the Right EV Charger for Your Needs
Selecting the ideal home EV charger requires careful consideration of several critical factors. For businesses like Xeravolt offering professional charging solutions, understanding these elements helps deliver optimal value to clients.
Connector types
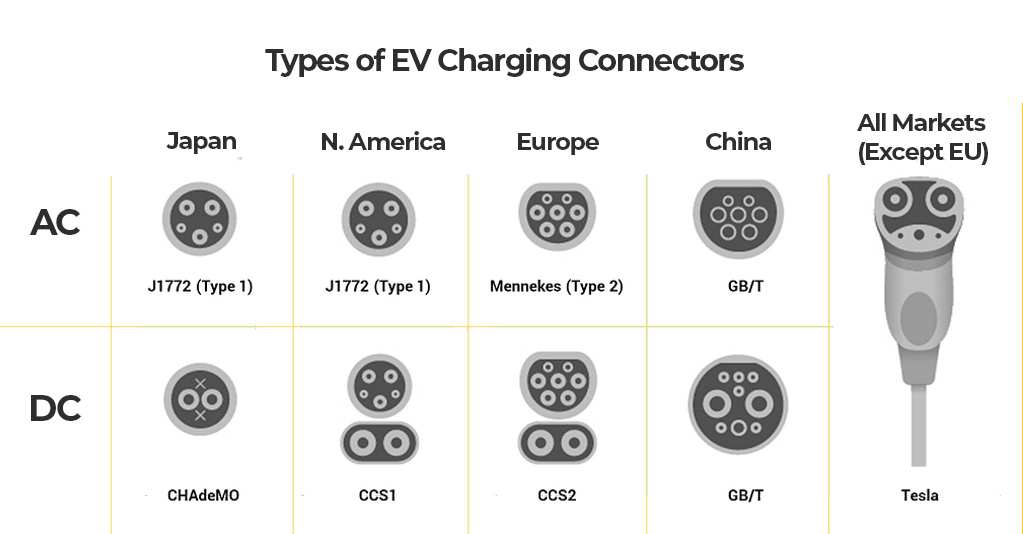
J1772 (J-Plug): This industry standard connector works with almost all non-Tesla electric vehicles manufactured before 2025. It’s designed for Level 1 and Level 2 charging, delivering up to 19.2 kW of power. J1772 offers widespread compatibility and proven reliability across numerous vehicle brands.
NACS (North American Charging Standard): Formerly Tesla’s proprietary connector, NACS is increasingly becoming the future industry standard with major automakers committing to its adoption for models from 2025 forward. NACS supports both AC and DC charging, enabling faster charging rates up to 250 kW.
CHAdeMO (Japan): A fast-charging standard developed in Japan, CHAdeMO delivers DC power up to 62.5 kW. While widely adopted by early EVs like the Nissan Leaf, its usage is declining globally in favor of newer, more versatile standards like CCS and NACS.
CCS1 (Combined Charging System Type 1 – North America): CCS1 builds on the J1772 connector by adding two extra pins for high-speed DC charging, supporting up to 350 kW. It’s a key standard in North America, compatible with a wide range of EVs from manufacturers like Ford, GM, and BMW.
CCS2 (Combined Charging System Type 2 – Europe): CCS2 integrates the European Type 2 (Mennekes) plug for AC with DC fast-charging capability. It’s the dominant standard in Europe and increasingly adopted in other regions. CCS2 supports high-power DC charging, with rates up to 350 kW.
Mennekes (Type 2 – Europe): This is the standard AC charging connector across Europe. It supports single-phase and three-phase power, delivering up to 43 kW depending on infrastructure and vehicle capability. Known for its durability and robust design.
GB/T (China): China’s national standard, GB/T has separate AC and DC connectors. The AC version supports up to 7.4 kW (single-phase) or higher with three-phase configurations, while the DC version can deliver up to 250 kW. It’s mandatory for all EVs sold in China.
For businesses installing charging infrastructure, adapters exist to ensure compatibility between connector types, though native connections are generally more reliable long-term.
Smart features to look for
Modern home EV chargers offer advanced capabilities that maximize efficiency:
- Power management features that adjust maximum amperage delivery
- Circuit sharing technology that intelligently manages power with other appliances
- Usage tracking and analytics for monitoring energy consumption
- Scheduled charging capabilities for off-peak electricity rates
- Access controls for multi-user environments
Wi-Fi connectivity enables remote management through smartphone apps, although this may be redundant for newer EVs with built-in scheduling capabilities. For commercial installations, these smart features provide valuable data and control options.
Weatherproofing and outdoor installation
Outdoor installation requires chargers specifically rated for weather exposure:
First, look for units with NEMA 4X ratings that protect against water, dust, and corrosion. Chargers installed outside must have weatherproof enclosures certified for continuous exposure to elements.
Furthermore, hardwired connections offer superior safety compared to plug-in models for outdoor installations. Professional electricians should always handle outdoor installations to ensure proper weatherproofing and compliance with safety regulations.
CE, UL and ENERGY STAR certifications

Certifications provide critical assurance of safety and efficiency:
In North America, all home EV chargers should be safety certified by nationally recognized testing laboratories such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or ETL (Intertek). Additionally, ENERGY STAR® certified chargers use approximately 40% less energy during standby compared to non-certified models, helping homeowners reduce unnecessary energy waste.
In Europe, chargers must carry the CE mark, indicating compliance with essential EU health, safety, and environmental standards. Many models also follow IEC 61851 protocols and may be independently tested by bodies like TÜV or DEKRA, adding further credibility.
Consequently, choosing certified equipment protects both the vehicle and home while maximizing energy efficiency. These certifications are non-negotiable elements for professional installations, demonstrating commitment to safety and quality standards.
Plan for Installation and Budgeting
Professional installation planning marks the final crucial step in your home EV charger journey. Let’s examine key considerations for implementation and financial planning.
Hardwired vs plug-in: Pros and cons
Hardwired installations connect directly to your electrical panel without using an outlet. This option offers several advantages:
- Supports higher charging speeds up to 19.2kW (vs 9.6kW maximum for plug-in models)
- Enhanced safety with fewer connection points and built-in GFCI protection
- Cleaner esthetic appearance without visible outlets
Conversely, plug-in chargers offer:
- Easier installation if you already have a compatible 240V outlet
- Greater flexibility when upgrading or relocating
- No permit requirements in some jurisdictions (unlike hardwired units)
Hiring a certified electrician
Professional installation isn’t merely recommended—it’s essential. When selecting an electrician:
Look for contractors with specific EV charging credentials such as EVITP certification. A qualified professional will:
- Perform mandatory load calculations to assess your electrical capacity
- Obtain necessary permits and complete required inspections
- Ensure installation meets local codes and safety standards
For businesses like Xeravolt, partnering with certified contractors creates a trustworthy installation network, requiring professionals with proper licensing, insurance ($1M liability coverage), and business credentials.
Home EV charger installation cost breakdown
Installation expenses typically fall between $799-$1,999, comprising:
- Charger hardware: $300-$1,200
- Basic installation labor: $400-$1,200
- Permit fees: $100-$200
- Electrical panel upgrades (if needed): $800-$2,000
- Wiring costs: Approximately $15-$25 per meter
Distance between your electrical panel and installation location significantly impacts overall cost.
Available tax credits and rebates
Currently, federal incentives include:
- 30% tax credit on equipment and installation costs up to $1,000 per charging port through December 2032
- Credit applies to charging equipment plus associated property directly supporting it
- File IRS Form 8911 to claim this non-refundable tax credit
Additionally, numerous state and utility rebates exist, often stackable with federal incentives. The Department of Energy maintains a searchable database of local incentives to further offset installation costs.
Optimize for Long-Term Use and Scalability
Investing in home EV charging infrastructure requires forward-thinking beyond initial setup. Effectively, businesses like Xeravolt must consider how their charging solutions accommodate long-term needs and evolving technology.
Scheduling and off-peak charging
Smart scheduling represents one of the most valuable features in modern home EV chargers. Around 85% of EV drivers choose home charging primarily because it allows strategic power management. Off-peak charging hours—typically between midnight and 7 a.m.—offer electricity at significantly reduced rates.
Most contemporary EV chargers include programming capabilities that enable users to:
- Set specific charging windows aligned with utility off-peak hours
- Automatically begin charging when electricity costs drop
- Integrate with time-of-use utility plans for maximum savings
Businesses implementing charging solutions should emphasize that scheduling features can reduce charging costs by up to 30% compared to standard rates. Indeed, these savings compound substantially for fleet operations or multi-vehicle households.
Monitoring usage with Wi-Fi apps
Wi-Fi-enabled home EV chargers provide unprecedented control through dedicated mobile applications. These smart monitoring systems deliver actionable insights including:
Real-time charging status updates, historical energy consumption tracking, and customizable charging limits to prevent overcharging—a feature that extends battery lifespan.
For commercial applications, these platforms support account sharing with multiple users, allowing businesses to manage multiple charging stations under a single dashboard. This administrative capability proves invaluable for corporate fleet management or multi-tenant properties.
Preparing for multiple EVs or future upgrades
As EV adoption accelerates, future-proofing becomes critical. Initially, consider these scalability strategies:
Power-sharing systems allow two EV chargers on a single circuit to communicate and intelligently distribute available capacity. Unlike fixed dual chargers, these systems dynamically allocate power based on each vehicle’s needs.
Load-balancing technology monitors whole-house electrical consumption and automatically adjusts charging rates to prevent circuit overloads. This intelligent management eliminates the need for costly panel upgrades in many cases.
For maximum flexibility, install electrical infrastructure that exceeds current requirements. A dedicated 100-amp subpanel in the garage creates capacity for future expansion without expensive rewiring. This approach proves cost-effective as households transition toward multiple electric vehicles.
Conclusion
Selecting the right home EV charger represents a critical decision for both residential and commercial applications. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored essential aspects that businesses must consider when implementing charging solutions. Therefore, companies like Xeravolt play a pivotal role in helping clients navigate these complex decisions.
Electrical assessment undoubtedly forms the foundation of any successful installation. Professional electricians must verify panel capacity, available circuits, and determine whether upgrades are necessary before proceeding. Additionally, understanding connector compatibility ensures future-proof installations as the industry transitions toward NACS standards.
Smart features certainly deliver significant value beyond basic charging functionality. WiFi connectivity, usage tracking, and scheduled charging capabilities allow businesses to optimize energy consumption and reduce operational costs. Subsequently, these intelligent systems provide invaluable data for fleet management and multi-tenant properties.
Professional installation remains non-negotiable for safety and reliability. Certified electricians ensure code compliance, proper permitting, and thorough testing of all systems. Meanwhile, available tax credits and rebates significantly offset initial investment costs, making comprehensive charging solutions more accessible.
Looking ahead, scalability must factor into any strategic charging infrastructure plan. Businesses installing multiple charging stations benefit from load-balancing technology and power-sharing systems that maximize existing electrical capacity. Consequently, these forward-thinking solutions eliminate costly retrofits as EV adoption accelerates.
Home EV charging continues evolving rapidly with advancing technology. Businesses partnering with experienced providers like Xeravolt gain access to cutting-edge solutions backed by professional expertise. The right charging infrastructure ultimately transforms from a simple amenity into a strategic asset that enhances property value while supporting sustainability goals.

